ArokaGO News
•May 28, 2024
Understanding Blood in Urine - A Possible Indicator of Bladder Cancer
The National Cancer Institute and the Department of Medical Services are issuing a critical warning regarding urinary symptoms, particularly if blood is present in the urine. This seemingly innocuous sign could signal a grave underlying condition, such as bladder cancer. Dr. Sakarn Bunnag, Deputy Director General of the Department of Medical Services under the Ministry of Public Health, Thailand stresses the urgency of seeking immediate medical attention upon noticing such symptoms, as they may indicate the presence of red blood cells in the urine.
The ArokaGO Reporter
May 28, 2024

The National Cancer Institute and the Department of Medical Services are issuing a critical warning regarding urinary symptoms, particularly if blood is present in the urine. This seemingly innocuous sign could signal a grave underlying condition, such as bladder cancer. Dr. Sakarn Bunnag, Deputy Director General of the Department of Medical Services under the Ministry of Public Health, Thailand stresses the urgency of seeking immediate medical attention upon noticing such symptoms, as they may indicate the presence of red blood cells in the urine.
The appearance of blood in the urine can manifest in various hues, ranging from fresh red to dark brown, and may even resemble the washing off of flesh or blood clots. In severe instances, blood clots can impede the urethra, causing difficulties in urination. However, smaller traces of blood may not be immediately apparent and may require laboratory testing for detection.
A myriad of factors can contribute to blood in the urine, including urinary stones, infections, enlarged prostates, or injuries. Alarmingly, approximately 20% of cases involving blood in the urine are linked to bladder cancer, especially when unaccompanied by pain. Hence, comprehensive diagnostic testing, encompassing urine microscopy and upper urinary tract X-rays, is imperative to pinpoint the root cause.
Dr. Promwong Ngamwutthiwong, Urological surgeon National Cancer Institute, Thailand, underscores the criticality of early detection and treatment for bladder cancer. Treatment modalities hinge on the cancer's extent and severity. While localized tumors may be addressed through minimally invasive procedures like Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TUR-BT), advanced cases may necessitate radical interventions to excise the bladder and adjacent lymph nodes.
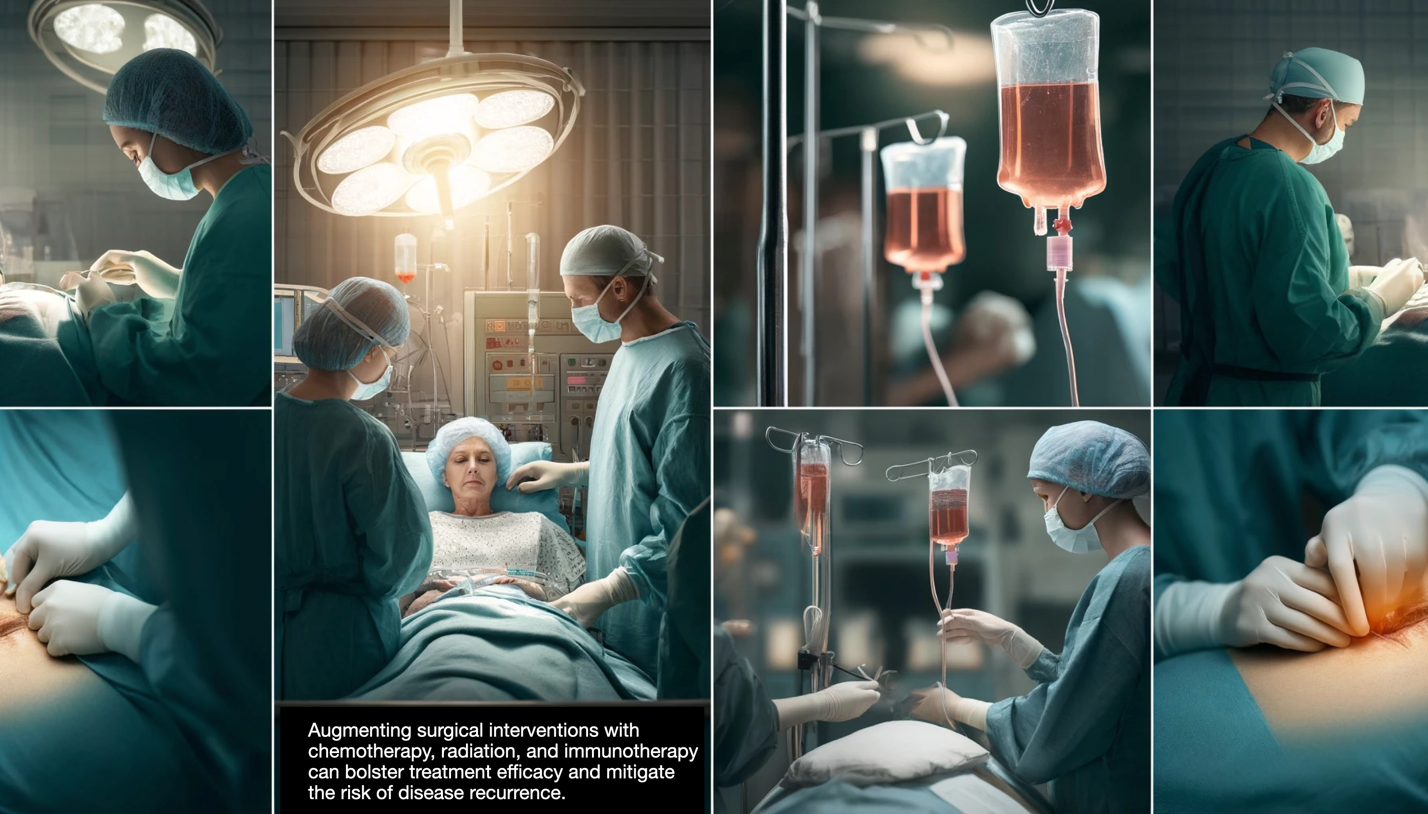
Augmenting surgical interventions with chemotherapy, radiation, and immunotherapy can bolster treatment efficacy and mitigate the risk of disease recurrence. Routine follow-up urine tests are indispensable for monitoring individuals with unresolved symptoms or predisposing factors for bladder cancer, such as smoking or chemical exposure.
While the presence of blood in urine may evoke alarm, early detection is pivotal for favorable treatment outcomes. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, characterized by regular exercise and abstention from smoking and processed foods, can mitigate the risk of bladder cancer and foster overall well-being.
For individuals seeking additional information or support, the National Cancer Institute offers invaluable resources and educational materials through their website: https://allaboutcancer.nci.go.th. Stay informed, proactive, and prioritize your health to effectively combat cancer.

ArokaGO Star Award Ceremony Highlights Industry Excellence and Seminar on Medical Liability Insurance and Case Studies
May 26, 2024

Protein Intake Crucial for Cancer Patients, Says Maha Vajiralongkorn Thanyaburi Hospital
June 9, 2024