
Thailand has emerged as a global leader in medical tourism, attracting over 3.5 million international patients annually. The country's appeal lies in its combination of high-quality healthcare services, affordability, and renowned hospitality.
Police General Hospital

Symptoms of Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis often progresses silently, particularly in its early stages. Typically, there are no noticeable symptoms until the condition has significantly worsened. As it advances, individuals may experience:
- Chronic back pain
- A hunched back
- Decreased height
- Bones that break more easily than normal, even without severe accidents
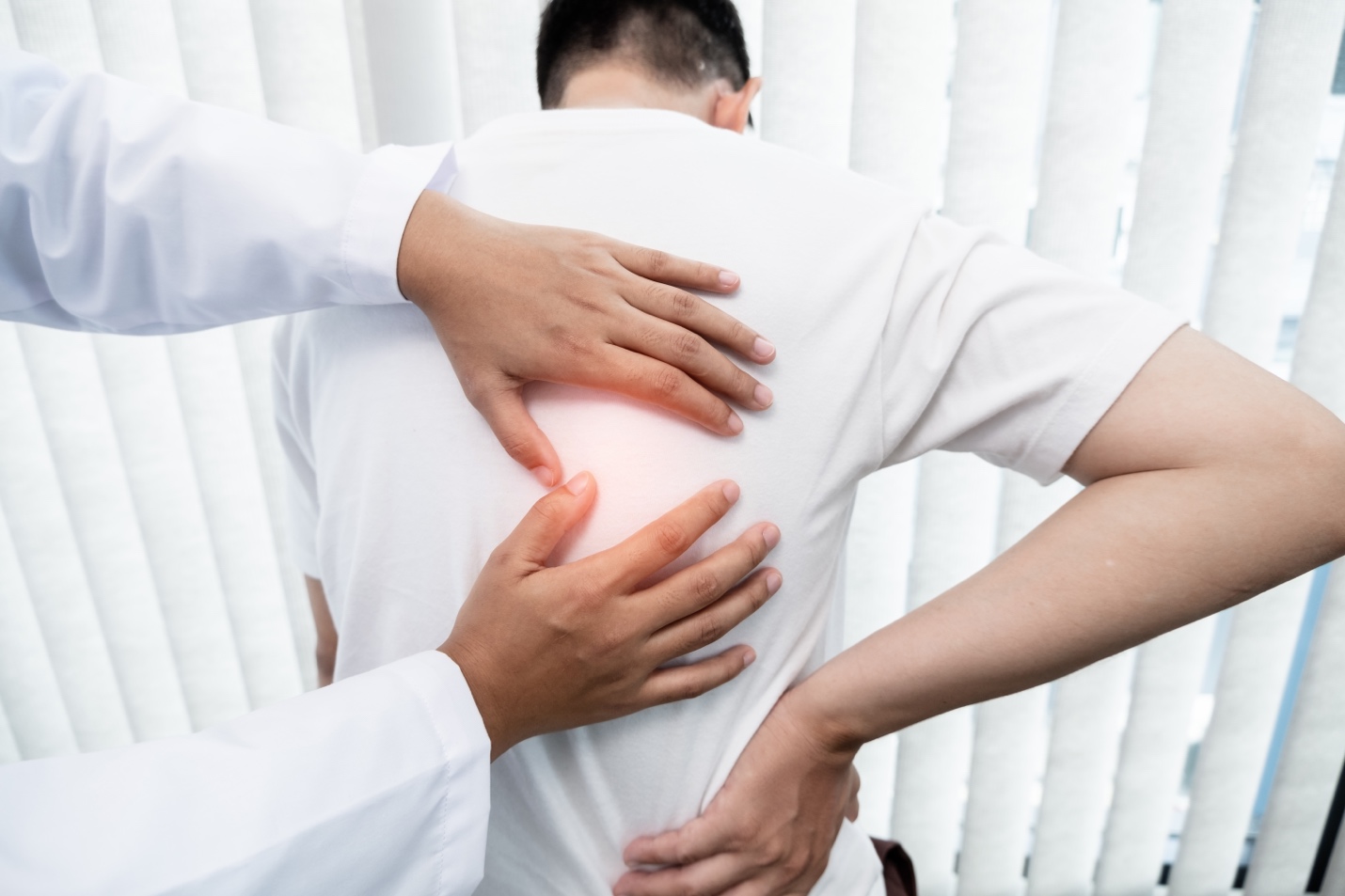
Diagnosis of Osteoporosis
The primary method for diagnosing osteoporosis is by measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA). The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies bone density values as follows:
- Normal Bones (Normal bone): Bone density values within 1 standard deviation (SD) compared to young adults (T-score > -1).
- Osteopenia (Thin bones): Bone density values between -1 SD and -2.5 SD compared to young adults (-2.5 < T-score < -1).
- Osteoporosis: Bone density values of -2.5 SD or lower compared to young adults (T-score < -2.5 SD).
- Severe Osteoporosis: Bone density values of -2.5 SD or lower, with a fracture, compared to young adults (T-score < -2.5 SD).
Indications for Bone Density Measurement
Bone density measurement is recommended for:
1. Women aged 65 years and older and men aged 70 years and older.
2. Women under 65 years and men under 70 years with at least one of the following risk factors:
- Women who have had both ovaries removed or experienced menopause before age 45.
- Women with estrogen deficiency before menopause for more than 1 year, except in cases of pregnancy and lactation.
- Individuals taking steroids for extended periods.
- Individuals with a family history of hip fractures.
- Postmenopausal women with a body mass index (BMI) of less than 20 kg/m².
3. Individuals with X-ray results showing a thin or deformed spine.
4. Individuals with a history of bone fractures from non-severe accidents.
5. Individuals whose height has decreased by more than 4 cm or more than 2 cm per year.
6. Individuals in the medium or higher risk group from screening with OSTA index, KKOS score, or nomogram.
Biochemical Markers and Their Limitations
Blood tests for biochemical markers of bone turnover, such as CTx, P1NP, and N-MID Osteocalcin, are not recommended for diagnosing osteoporosis. These markers can be influenced by many factors and may show abnormalities due to various conditions other than osteoporosis. However, they can complement bone density tests to assess fracture risk and track treatment efficacy. It is recommended to check these markers before starting osteoporosis medication and re-evaluate them after 3, 6, and 12 months of treatment. This approach helps gauge the response to treatment more quickly than relying solely on DXA.
References
National Osteoporosis Foundation. Physician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Washington, DC: National Osteoporosis Foundation 1999.
NIH Consensus Development Panel on Osteoporosis Prevention, Diagnosis and Therapy. Osteoporosis prevention, diagnosis and therapy. JAMA 2001; 285:785-795.
Medical practice recommendations for osteoporosis care. Osteoporosis Foundation of Thailand, 2021.
Source: DoctorWat
Note: Translated and compiled by ArokaGO Medical Content Team.
Discover the secrets to effective health care planning in our article.

Thailand has emerged as a global leader in medical tourism, attracting over 3.5 million international patients annually. The country's appeal lies in its combination of high-quality healthcare services, affordability, and renowned hospitality.

When I was a child, I heard a story that has lingered in my memory ever since. A fire had broken out in a quiet village, and amid the panic, one man rushed back into his burning home—not to find his family or save something irreplaceable, but to carry out a large water jar. He managed to escape, jar in tow, but as he stood in the ashes later, he was struck with confusion. How had he carried something so heavy on his own? And more troubling still—why had he instinctively grabbed the jar instead of thinking about his family’s safety?

Facelifts are among the most effective procedures to rejuvenate the face and reverse signs of aging. However, choosing the right facelift technique — tailored to your facial structure, age, and expectations — is essential to achieving natural, long-lasting results.
ALINE Clinic