What is the HIS System? An In-depth Look at Its Benefits

The HIS (Hospital Information System) is a type of hospital management system (HMS) designed to store, manage, and transmit large volumes of data both within and outside a hospital. This system allows hospital executives to allocate resources efficiently, increasing operational efficiency and enabling swift, modern patient care. Let's delve into the HIS system, its components, and its numerous benefits.
Understanding the HIS System
The HIS system employs information technology (IT) to manage extensive databases, enabling healthcare providers such as doctors and nurses to access patient health information from the hospital database or other healthcare facilities. This access facilitates quick patient care planning and assessment.
Moreover, the HIS system supports various hospital departments, fostering efficient operations and systematic coordination. Key departments that benefit from the HIS system include:
- Healthcare System
- Laboratory Testing System
- X-ray System
- Nutritional System
- Maintenance System
- Pharmacy System
- Social Welfare System
- Treasury System
- Personnel System

Components of the HIS System
The effective operation of the HIS system relies on the seamless integration of four critical components:
1. Hardware
- All IT equipment related to hospital operations, such as computers, notebooks, smartphones, tablets, servers, clients, and network systems, fall under this category.
2. Software
- Operating Systems: These run on hardware devices, including Windows, macOS, Linux for computers, and Android and iOS for smartphones and tablets.
- Utility Programs: These enhance computer efficiency. Examples include File Manager, Disk Defragmenter, Anti Virus Programs, and File Compression Utilities.
- Applications: Specific programs for hospital systems, such as the Hospital Information System (HIS), Electronic Medical Records (EMR), and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP).
3. Peopleware
- Individuals involved in using the entire system, including system managers, system analysts, programmers, and daily users like doctors, nurses, and hospital personnel across various departments.
4. Data
- All information within the hospital stored in the system, including patient history, medical information, laboratory data, and medication information.

Benefits of Using an HIS System
Managing large amounts of data in a hospital setting can be complex and time-consuming, especially when done manually. The HIS system provides a solution by utilizing IT to manage data more efficiently, reducing the potential for errors and improving overall organizational collaboration. Here are some key benefits:
1. Data Analytics
- Existing data can be analyzed to plan operations and develop faster treatment methods by combining treatment data from multiple patients.
2. External Collaboration
- The HIS system facilitates the exchange of information and general health records between departments and external health agencies, helping manage scattered patient health information.
3. Efficient Information Preparation
- HIS simplifies the preparation of reports for each department, whether daily, monthly, or yearly, making administrative tasks more efficient.
4. Streamlined Operations
- Daily operations such as scheduling surgeries, work shifts, and clinic appointments become smoother, ensuring hospital personnel can work more effectively.
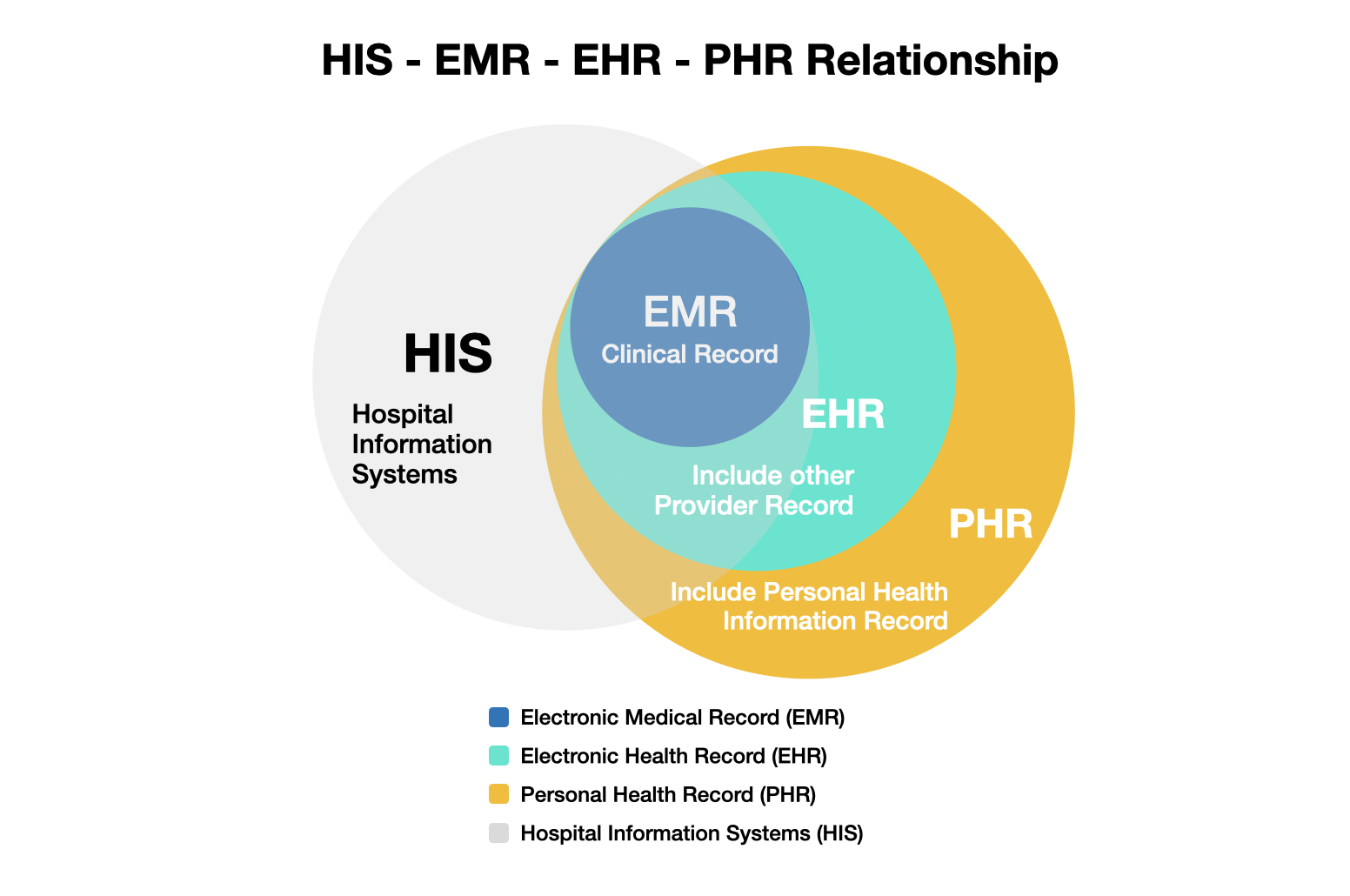
Components of a Hospital Information System
The HIS system consolidates all hospital information, aiding executives in planning, development, strategic planning, and policy-making. The system's components are divided into three major groups:
1. Medical Care
- Facilitates both patients and medical personnel by linking patient information from various departments, enabling quick and convenient service. Key sub-systems include:
- Medical Records and Statistics System
- Outpatient Work System
- Inpatient Work System
- Pharmacy Work System
- Pathology/Autopsy Work System
- Radiology System
2. Administrative and Academic
- Supports hospital administration and academic research by providing comprehensive data management and reporting tools.
3. Medical Engineering
- Ensures the hospital's technical infrastructure is maintained, supporting the smooth operation of all medical and administrative functions.
In summary, the HIS system is a crucial tool in modern healthcare, enhancing efficiency, reducing errors, and improving patient care through effective data management and technology integration.
For further information or to inquire about services, please contact us at contact@arokago.com.
Share this article
More Articles
Discover more insights on health care and medical tourism.

What is the Nipah Virus ? Know It, Prevent It - No Need to Panic
The Nipah virus is a type of virus that can be transmitted from animals to humans. In some cases, it can also spread from person to person. It is considered an emerging infectious disease that has been identified only in the past few decades and has caused occasional outbreaks in certain countries.

What Causes Pimples Around the Mouth. How Can They Be Treated?
Acne around the mouth is a common skin problem that can make many people feel uncomfortable and lose confidence. The causes of acne in this area can be complex, involving hormones, skincare habits, and things that frequently come into contact with the face. This article explains why pimples appear around the mouth and the effective ways to treat them.

How food and Lifestyle Affect Egg and Sperm Quality
Many couples try to conceive for a long time. The quality of eggs and sperm does not depend on age alone. It is deeply influenced by what we eat, how we live, and how well we take care of our bodies every day.